Introducing Fast Sync
A Casper Network requires new nodes to download and execute every block to join the network. From genesis (start of the Mainnet), the node executes each transaction in every block. This process continues until the node has arrived at the current state of the blockchain. Syncing a node this way can take a very long time.
We have introduced a fast syncing process (fast sync) to provide a faster alternative to joining a Casper network. Fast sync does not start syncing at the genesis block; instead, the operator verifies a recent block and provides a trusted hash to the node software. The global state, account balances, and all other on-chain information is the storage layer of the blockchain and is massive in size, so fast sync downloads the global state of only the most recent block. The following section briefly describes the fast sync process.
How Fast Sync Works
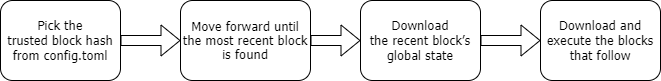
For fast sync, operators must provide the trusted hash of a block in the config.toml file. An example can be found here.
Fast sync uses this trusted block as part of the cryptographic verification for the later blocks. The node downloads the trusted block first, then newer blocks up to and including the most recent block from the current era. For example, if the trusted hash is 5 hours old, it will first download that block, then newer blocks, until it arrives at one that is only a few minutes old. It then downloads the newer block's global state. Finally, it executes all the blocks the network created while the download was in progress until it is entirely in sync.