Monitoring Events with the Casper Sidecar
Monitoring and Consuming Events
The Casper platform uses event streaming to signal state changes in smart contracts and nodes. Using the Casper Sidecar service and client-side SDKs, dApps actively listening for emitted events can consume them and perform actions based on event data.
Smart contracts can also emit contract-level events, as explained here. DApps can consume these events by listening to the event stream, detecting TransactionProcessed events, and parsing the messages array storing String-representations of the emitted events.
The Casper Sidecar
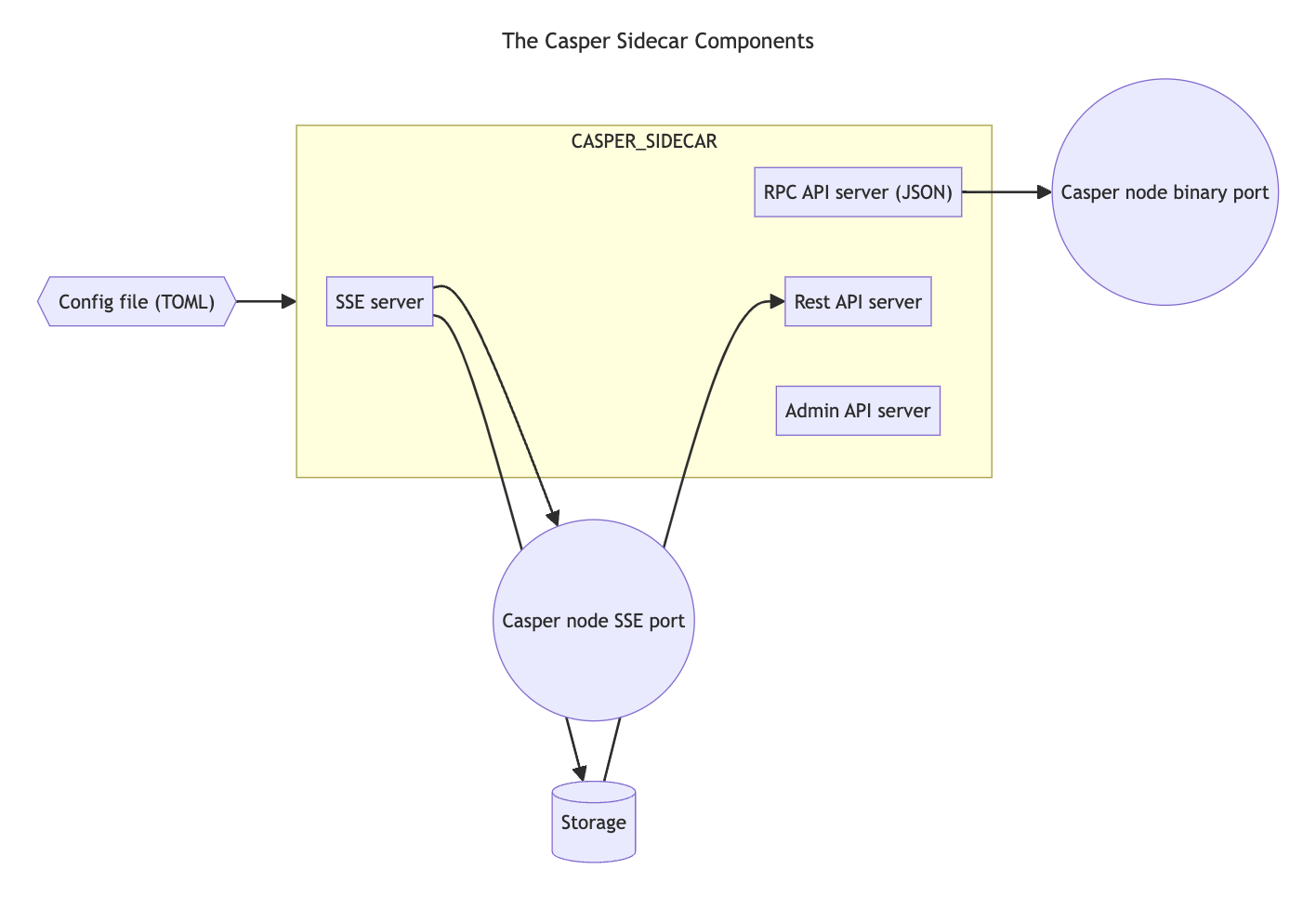
The Casper Sidecar is an application running alongside the node process. It allows subscribers to monitor a node's event stream, query stored events, and query the node's JSON-RPC API, thus receiving faster responses and reducing the load placed on the node. The Sidecar supports the following functionalities:
- A server-sent events (SSE) endpoint with an
/eventsendpoint streaming events from all the connected nodes. The Sidecar also stores these events. - A REST API server that allows clients to query stored events.
- A JSON-RPC API to interact with a Casper node.
- Legacy emulation for clients using older versions of the SSE API.
Visit GitHub for the latest source code and information on:
- System architecture
- Configuring the Sidecar
- Running and testing the Sidecar
- Swagger documentation for its REST API
- OpenAPI schema for the JSON-RPC API
- Troubleshooting tips
The Event Stream
Casper nodes offer an event stream API that returns server-sent events (SSEs) with JSON-encoded data. The Sidecar reads the event stream of all connected nodes, acting as a passthrough and replicating the SSE interface of the connected nodes.
The Sidecar can:
- Republish the current events from the node to clients listening to Sidecar's SSE API.
- Publish a configurable number of previous events to clients connecting to the Sidecar's SSE API with
?start_from=query (similar to the node's SSE API). - Store the events in external storage so clients can query them via the REST API.
The Sidecar also provides an endpoint for Sidecar-generated events that can be useful, although the node did not emit them.
To summarize, events are divided into two categories and emitted on their respective endpoints:
- Node-generated events - All events coming from connected node(s) are emitted on the
eventsendpoint. The default URL to consume these events on a Mainnet or Testnet node is usuallyhttp://HOST:19999/events/. This URL depends on how the Sidecar was configured on the node. - Sidecar-generated events - The Sidecar also emits events on the
events/sidecarendpoint, designated for events originating solely from the Sidecar service. The URL to consume these events using Sidecar on a Mainnet or Testnet node is usuallyhttp://HOST:19999/events/sidecar/. This URL depends on how the Sidecar was configured on the node.
The Casper Sidecar Usage Guide describes each event type in detail.
Listening to the Event Stream
Set up an event listener in your dApp using the following code to consume the event stream. The NODE_ADDRESS is the address of the node where the Sidecar was installed. The PORT is the address where the Sidecar streams events. It is 19999 by default, but you must find out how the Sidecar was configured.
- JavaScript
- Python
- cURL
const { EventStream, EventName } = require("casper-js-sdk");
const es = new EventStream("http://NODE_ADDRESS:PORT/events/");
es.start();
es.subscribe(EventName.EVENT_NAME, eventHandler);
const eventHandler = (event) => {
console.log(event);
};
from pycspr import NodeClient, NodeConnection, NodeEventType
def eventHandler(event):
print(event)
client = NodeClient(NodeConnection(host = "NODE_ADDRESS", port_rpc = "PORT"))
client.get_events(eventHandler, NodeEventType.EVENT_NAME)
curl -s http://NODE_ADDRESS:PORT/events/
You can find node addresses of active online peers to replace NODE_ADDRESS, by navigating to cspr.live for Mainnet and testnet.cspr.live for Testnet.
Replace EVENT_NAME with one of the event types listed below.
Detecting Contract-Level Events
The Sidecar streams messages emitted by a contract in a human-readable format. These messages are visible as part of the TransactionProcessed event after the corresponding block is processed and added to the blockchain. For more details, see Verifying a Topic and Verifying a Message.
Reacting to Events
An application may parse each event needed for its use case and respond accordingly. Each event type contains additional data that might help decide whether to take action. For example, TransactionAccepted events contain the account's public key that submitted the transaction, the contract address, and more. This information can help determine how to proceed.
- JavaScript
- Python
const eventHandler = (event) => {
if (event.body.TransactionAccepted.header.account == "012481699f9231e36ecf002675cd7186b48e6a735d10ec1b30f587ca716937752c") {
// Perform an action
}
};
def eventHandler(event):
if event["TransactionAccepted"]["header"]["account"] == "012481699f9231e36ecf002675cd7186b48e6a735d10ec1b30f587ca716937752c":
# Perform an action
Unsubscribing from Events
In many cases, an application may need to unsubscribe after a particular time or may want to unsubscribe from some events but not others. The Casper SDKs provide this ability with the unsubscribe function:
- JavaScript
es.unsubscribe(EventName.EVENT_NAME);
EVENT_NAME- One of the different event types emitted by a Casper node.
Stopping the Event Stream
A dApp may cease listening to all events using the stop function:
- JavaScript
es.stop();
Replaying the Sidecar Event Stream
This command will replay the event stream from an old event onward. Replace the NODE_ADDRESS, PORT, and ID fields with the values of your scenario.
- cURL
curl -s http://NODE_ADDRESS:PORT/events?start_from=ID
Example:
curl -sN http://65.21.235.219:19999/events?start_from=29267508
Note that certain shells like zsh may require an escape character before the question mark:
curl -sN http://65.21.235.219:19999/events?start_from=29267508
The server will replay all the cached events if the ID is 0 or if you specify an event ID already purged from the cache.
The JSON-RPC API
The Sidecar also offers a JSON-RPC API server for clients to interact with a Casper network. It is a JSON bridge between end users and a Casper node's binary port, forwarding requests to the Casper node's binary port. For more details on how the JSON-RPC API works, see the JSON-RPC README.
The REST API
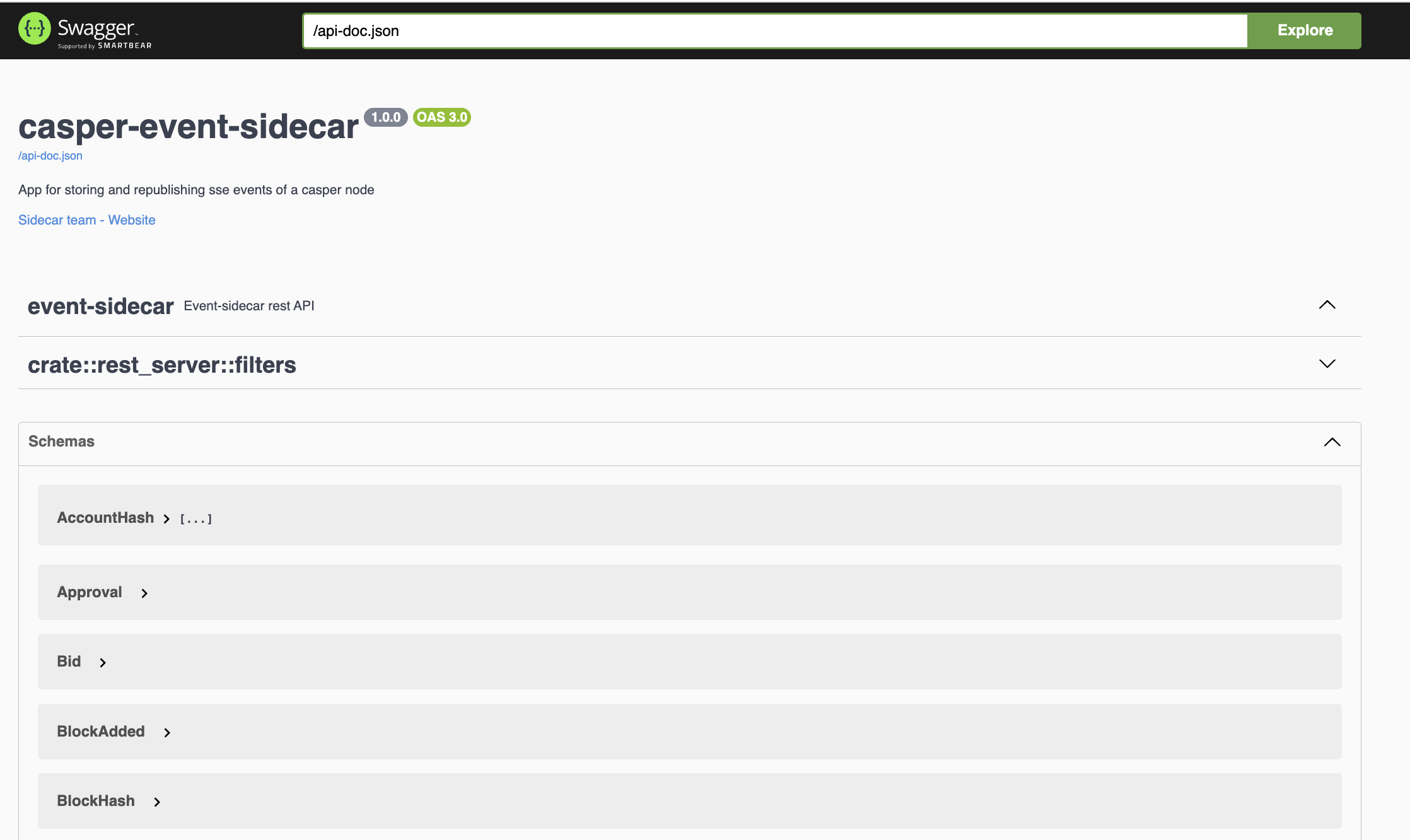
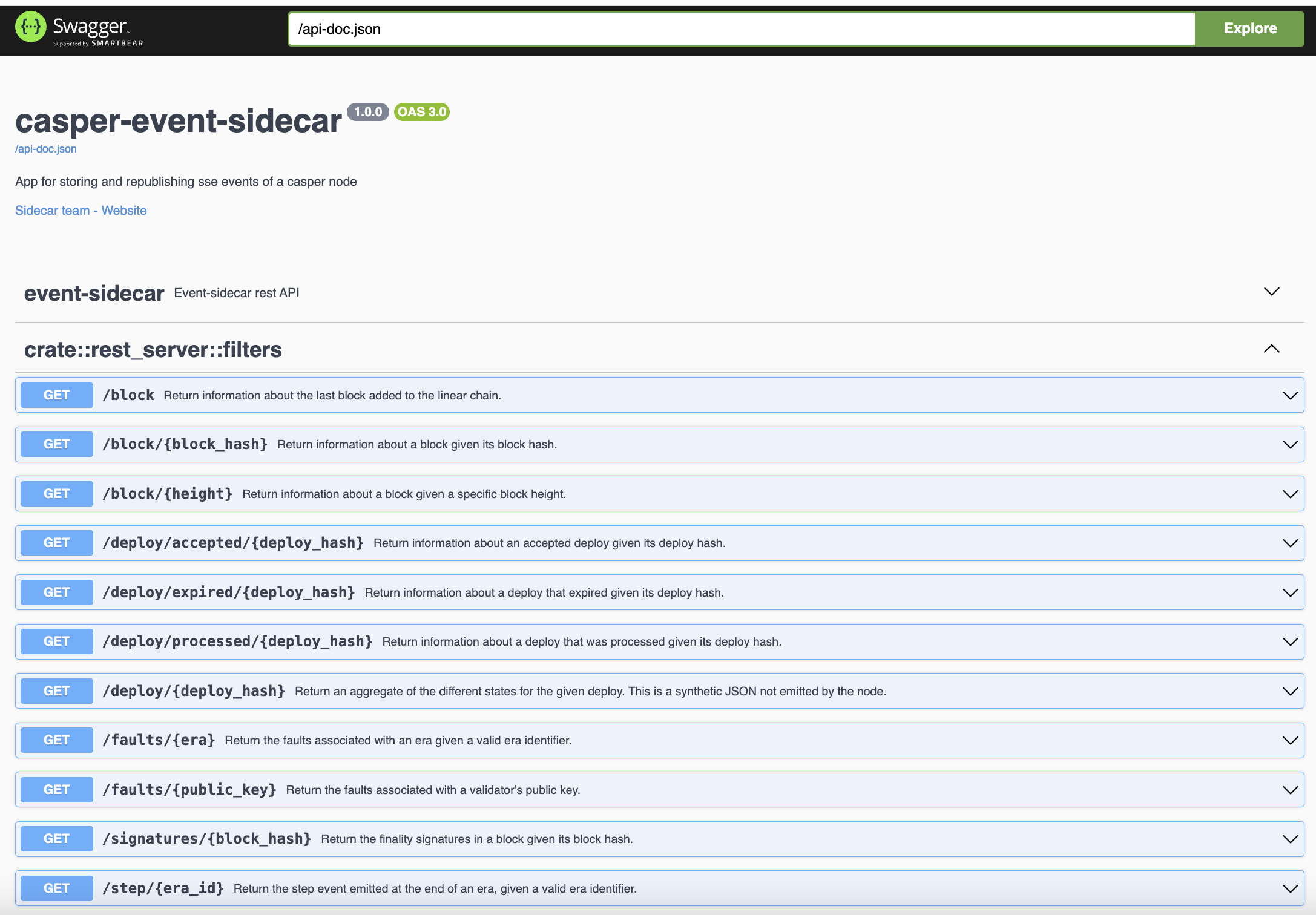
The Sidecar offers a REST API to query stored events. You can discover the specific endpoints of the REST API using OpenAPI and Swagger. The usage instructions in the repository provide more details.
Troubleshooting Tips
For troubleshooting tips, visit Github.