Authorization Keys
This topic explains the usage of authorization keys when signing a transaction and how to access them from a smart contract. Try the Working with Authorization Keys tutorial for an example.
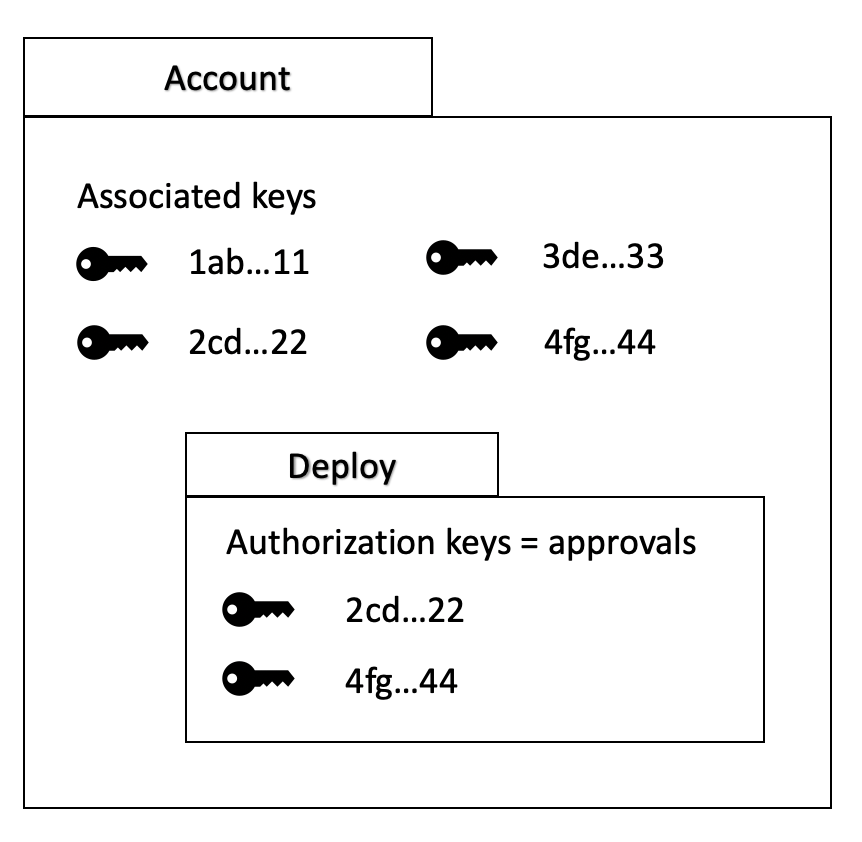
Associated Keys vs. Authorization Keys
Let's review the difference between associated keys to an Account and authorization keys for a transaction.
- Associated keys are public keys that are associated with a given account. To understand associated keys and how they are linked to an account, read about associated keys and weights and try the Two-Party Multi-Signature tutorial.
- Authorization keys are public keys used to sign a transaction and are listed in the transaction's
approvals. Authorization keys are a subset of the associated keys of the account under which the transaction is executed. - When a node receives a transaction, it checks that the transaction has the required authorization keys under
approvalsbefore including it in a block. - Different transactions executing the same smart contract can have different authorization keys.
Here is a sample JSON representation of an Account's associated keys:
"associated_keys": [
{
"account_hash": "account-hash-1ab…11",
"weight": 1
},
{
"account_hash": "account-hash-2cd…22",
"weight": 1
},
{
"account_hash": "account-hash-3de…33",
"weight": 1
},
{
"account_hash": "account-hash-4fg…44",
"weight": 1
}
], ...
Here is a sample JSON representation of a transaction's authorization keys:
"approvals": [
{
"signer": " 2cd...22",
"signature": "02df8c...f481"
},
{
"signer": "4fg...44",
"signature": "02ef21...756a"
}
]
Accessing Authorization Keys from a Smart Contract
Contract code can retrieve the set of authorization keys for a given transaction by calling the contract_api::runtime::list_authorization_keys function, which returns the set of account hashes representing the keys used to sign the transaction.
When to Use Authorization Keys
Authorization keys give developers more fine-grained control within their smart contracts. For example, developers can define a hierarchy within an account's associated keys. Then, they can use this hierarchy and the current execution's authorization keys to limit access for certain operations.
Try the Working with Authorization Keys tutorial to view an example workflow.